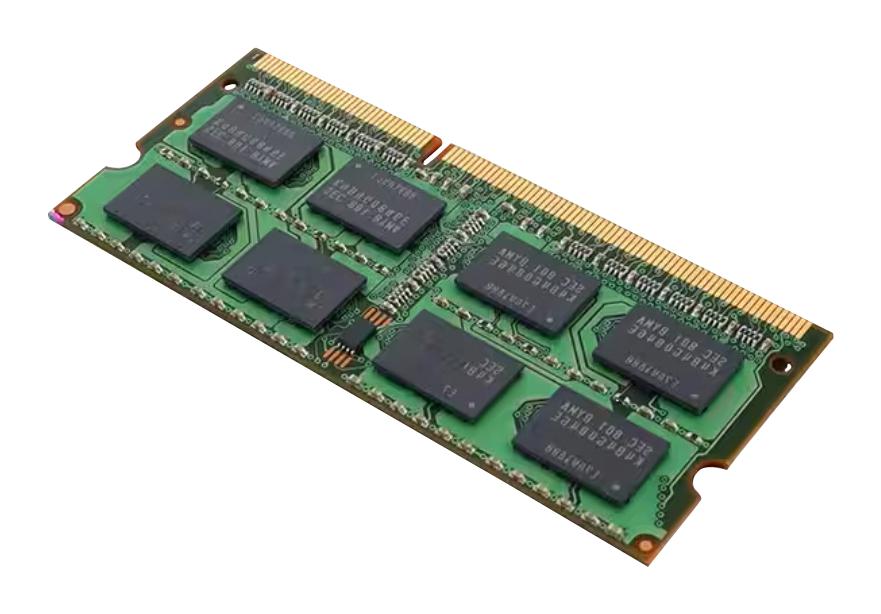
RAM (Memory)
$45.00
RAM (Random Access Memory) is the temporary memory of a computer that stores active programs and data for quick access, enabling faster performance, smooth multitasking, and efficient processing.
When we talk about computer performance, one of the most crucial components that comes into play is RAM (Random Access Memory). Many people often hear terms like “8GB RAM,” “DDR4,” or “memory upgrade” when buying a computer or smartphone, but not everyone truly understands what RAM does and why it’s so important. In simple terms, RAM can be thought of as the short-term memory of your computer. Just like the human brain uses short-term memory to recall immediate information quickly, computers use RAM to store data that is currently in use so that the processor can access it instantly. Without RAM, computers would rely solely on storage devices like hard drives or SSDs, which are far slower compared to the lightning-fast nature of RAM.
What is RAM?
RAM stands for Random Access Memory, and it is a type of volatile memory. Volatile means that the data stored inside RAM is temporary and disappears as soon as the device is turned off or restarted. Unlike storage drives that permanently save files such as documents, photos, and videos, RAM only holds the data that is currently being used by the operating system, applications, and programs.
Think of it like this: If your computer was a desk, the hard drive would be the filing cabinet where you store all your papers and folders. RAM, on the other hand, is the desk surface where you spread out the papers you’re working on right now. The bigger your desk (more RAM), the more tasks you can handle simultaneously without feeling cramped.
Why is RAM Important?
RAM plays a key role in determining how fast and efficient your device feels. Here are some reasons why it matters so much:
Multitasking Power:
More RAM allows you to run several programs at once without slowing down your computer. For instance, you can browse the web with multiple tabs open, listen to music, and work on a Word document all at the same time if you have enough memory.
Speed and Responsiveness:
RAM provides the processor with quick access to data. Unlike storage drives, which can be relatively slow, RAM works at incredibly high speeds. This means applications launch faster, files open more quickly, and tasks complete without long delays.
Smooth Gaming Experience:
For gamers, RAM is critical. Modern video games require large amounts of memory to load textures, maps, and in-game assets. Insufficient RAM can result in lag, stuttering, or crashes, while having enough RAM ensures smoother gameplay.
Efficient Software Performance:
Applications like photo editing, video rendering, and 3D modeling need substantial memory. Professionals working in creative industries often upgrade their RAM to handle large projects without slowdowns.
How Does RAM Work?
Whenever you launch a program, such as Microsoft Word or Google Chrome, the system loads parts of that program into RAM so the processor can quickly access the data. Without RAM, the system would have to constantly fetch data from the storage drive, which is much slower.
RAM modules are connected directly to the motherboard and communicate with the CPU (Central Processing Unit). The speed at which RAM can read and write data is measured in MHz (megahertz), while the size or capacity is measured in gigabytes (GB) or terabytes (TB) for high-end servers.
Types of RAM
There are different generations and types of RAM, each improving in terms of speed, efficiency, and capacity.
DRAM (Dynamic RAM):
The most common type of RAM used in computers. It requires constant refreshing of data to retain information.
SRAM (Static RAM):
Faster and more expensive than DRAM, usually found in CPU caches rather than as main system memory.
DDR (Double Data Rate) RAM:
This is the most widely used version in modern computers. Over the years, different versions have been released:
DDR2 – Older and slower.
DDR3 – Popular for many years.
DDR4 – Standard in most modern PCs.
DDR5 – The latest, offering even faster performance and higher efficiency.
VRAM (Video RAM):
A special type of RAM used by graphics cards to store image data and textures for rendering. Essential for gaming and graphic-intensive tasks.
Mobile RAM (LPDDR):
Low-power RAM used in smartphones and tablets to save battery life while still delivering good performance.
How Much RAM Do You Need?
The amount of RAM you need depends on what you use your device for:
Basic Usage (Web browsing, email, office work): 4GB – 8GB is sufficient.
Gaming: At least 16GB for modern games.
Professional Work (Video editing, 3D modeling, large datasets): 32GB or more.
Servers and High-Performance Computing: 64GB, 128GB, or even several terabytes depending on the workload.
Upgrading RAM – Does It Help?
Upgrading RAM is one of the easiest and most cost-effective ways to boost computer performance. If your computer struggles with multitasking or runs slowly when you open multiple programs, adding more memory can make a noticeable difference. However, RAM alone cannot solve every problem—other components like the CPU and SSD also play important roles.
Common Misconceptions About RAM
More RAM Always Equals Better Performance:
Not always. If your system already has enough RAM for the tasks you’re running, adding extra won’t make it faster. For example, upgrading from 16GB to 32GB won’t improve performance for basic web browsing.
RAM Stores Files Permanently:
This is incorrect. RAM is temporary memory. Once the system powers off, all data in RAM is erased. That’s why you need a storage drive to keep your files permanently.
All RAM is the Same:
RAM comes in different speeds and generations. Using incompatible or mismatched RAM sticks can lead to system instability. Always ensure the RAM type matches your motherboard.
Future of RAM
With the rise of AI, cloud computing, virtual reality, and big data, the demand for faster and more efficient memory is constantly growing. Technologies like DDR5 and beyond are being developed to handle the ever-increasing workload. Additionally, hybrid memory solutions like Intel Optane and persistent memory are bridging the gap between storage and RAM, offering both speed and data retention.
Real-Life Analogy for RAM
Imagine you are studying at a desk. The desk size determines how many books and notes you can keep open at once. If your desk is small, you’ll constantly have to put books back into the shelf (hard drive) to make space, slowing you down. But if you have a large desk (more RAM), you can spread out all the materials you need and work faster without interruption.
Conclusion
RAM (Random Access Memory) is truly the short-term brain of a computer. It doesn’t store information permanently but plays a crucial role in determining how fast and efficiently your system performs. From basic browsing to high-end gaming and professional editing, having the right amount and type of RAM can make a world of difference. As technology continues to evolve, RAM will keep becoming faster, more efficient, and capable of handling the complex demands of modern computing.
In short, without RAM, even the most powerful processor would feel sluggish, and multitasking would be nearly impossible. It’s one of the unsung heroes inside your device, silently ensuring that everything runs smoothly.
Fast Dispatch – Orders are processed within 24–48 hours after confirmation.
Secure Packaging – All products are packed safely to avoid damage during shipping.
Estimated Delivery – Standard delivery usually takes 3–7 business days depending on your location.
Tracking Available – Once your order is shipped, you’ll receive a tracking link via email/SMS.










Reviews
There are no reviews yet.